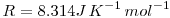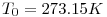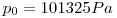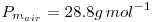Concentration conversion
Definitions
Concentration in parts per million (in volume)
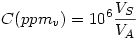
where 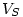 is the volume of the specie
is the volume of the specie 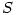 and
and 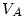 is the volume of the air. Using the perfct gas law:
is the volume of the air. Using the perfct gas law:
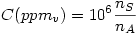
where 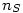 is the number of moles of the specie
is the number of moles of the specie 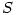 and
and 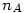 is the number of moles of air.
is the number of moles of air.
Conversions
from 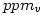 to
to 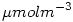
The conversion between 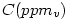 and
and 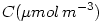 can be obtained invoking the he perfct gas law:
can be obtained invoking the he perfct gas law:
pV=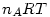
where R is the universal gas constant and thus:
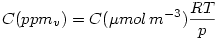
Note that using 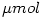 eliminates the factor
eliminates the factor 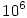 .
.
from 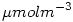 to
to 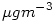
It is sufficient to multiply 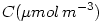 by the molecular weight (in
by the molecular weight (in 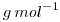 ) of the chemical specie:
) of the chemical specie:
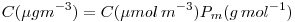
from 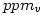 to
to 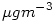
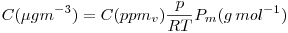
practical formula using standard atmosphere
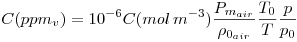
where: